| Section 5.3: Bullet Text Study Guide |
Contemporary Hardware Platform Trends
While the cost of computing has fallen, IT infrastructure expenditures have grown due to the rising cost of computing services, software, and the increase in intensity and sophistication of computing.
Telecommunications and computing platforms have converged: at the client level, with the merging of PDAs and cell phones, and at the server and network level, with the rise of Internet telephony.
Grid computing utilizes the idle computational resources of separate, geographically remote computers to create a single virtual supercomputer. In this process, a server computer breaks data and applications into discrete chunks that are parceled out to the grid's machines. Grid computing offers increased cost savings, computational speed and agility.
On-demand computing, or utility computing, refers to firms off-loading peak demand for computing power to remote, large-scale data processing centers. This allows firms to reduce their investment in IT infrastructure by investing in only as much computing power as needed on average and paying for additional power on an as-needed basis. This arrangement offers firms much greater agility and flexibility in their infrastructure.
Autonomic computing is an industry-wide effort to develop systems that can configure, optimize, repair, and protect themselves against intruders and viruses, in an effort to free system administrators from routine system management, reduce costly system crashes. Today's virus software with automatic virus updates is one example of autonomic computing.
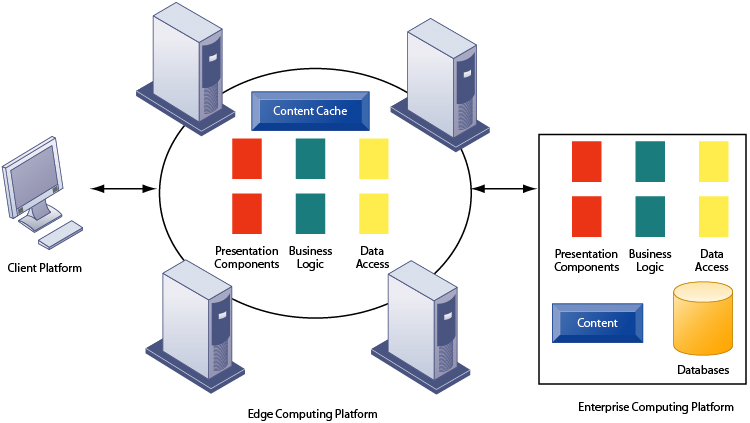
Edge computing is a multi-tier, load-balancing scheme for Web-based applications in which parts of the Web site content and processing are performed by smaller, less expensive servers located near the computer. In an edge computing platform client requests are initially processed by the edge servers, which may deliver static presentation content, reusable code, while database and business logic components are delivered by the enterprise servers.
Figure 5-11
 |
|
- Virtualization is the process of presenting a set of computing resources (such as computing power or data storage) so that they can all be accessed in ways that are not restricted by physical configuration or geographic location. Server virtualization enables companies to run more than one operating system at the same time on a single machine. Most servers run at just 10 to 15 percent of capacity, and virtualization can boost utilization server utilization rates to 70 percent or higher.
- A multicore processor is an integrated circuit that contains two or more processors. This technology enables two or more processing engines with reduced power requirements and heat dissipation to perform tasks faster than a resource-hungry chip with a single processing core.